Using Multiple DbContext on .NET 6 Web API With Repository Pattern
Hello, I this article, I will show how to use of multiple DbContext in an ASP.NET Web API (.NET 6.0) project. We will connect to 2 different databases by changing the DbContext. Now let’s create ASP.NET Web API (.NET 6) project. Secondly, we will install the EntityFramework packages.
1
2
3
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore -Version 6.0.4
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -Version 6.0.4
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools -Version 6.0.4
We will create the DbContext classes when the package installation is complete. Create three classes are named DbOneContext, DbTwoContext and BaseContext to the Data folder.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace MultipleDbContext.Data;
public class BaseContext : DbContext
{
public BaseContext(DbContextOptions options): base(options)
{
}
}
We will update DbOneContext and DbTwoContext concrete classes which inherits BaseContext.
DbOneContext:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace MultipleDbContext.Data;
public class DbOneContext : BaseContext
{
public DbOneContext(DbContextOptions<DbOneContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
}
DbTwoContext:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace MultipleDbContext.Data;
public class DbTwoContext : BaseContext
{
public DbTwoContext(DbContextOptions<DbTwoContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
}
After creating the DbContext classes, we will add DbOneContext and DbTwoContext are connectionstrings to the appsettings.json file.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DbOneContext": "Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=DBONE;User ID=sa;Password=Pw123456",
"DbTwoContext": "Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=DBTWO;User ID=sa;Password=Pw123456"
}
}
We will add DbContext classes info to Program.cs file.
1
2
3
4
5
builder.Services.AddDbContext<DbOneContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DbOneContext")));
builder.Services.AddDbContext<DbTwoContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DbTwoContext")));
Create a Models named folder and add a Book class.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
namespace MultipleDbContext.Models
{
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Anchor { get; set; }
}
}
Then we will add the Book entity class in BaseContext.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using MultipleDbContext.Models;
namespace MultipleDbContext.Data;
public class BaseContext : DbContext
{
public BaseContext(DbContextOptions options): base(options)
{
}
public DbSett<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
We will create a class called DbContextFactory in the Data folder. In this class we will return the BaseContext object with the contextName value inside an IDictionary. In this way, we will have made a development in accordance with SOLID principles.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
namespace MultipleDbContext.Data
{
public class DbContextFactory
{
private readonly IDictionary<string, BaseContext> _context;
public DbContextFactory(IDictionary<string, BaseContext> context)
{
_context = context;
}
public BaseContext GetContext(string contextName)
{
return _context[contextName];
}
}
}
Now we can create the Repository structure. Create IBookRepository interface under the Repository folder.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
using MultipleDbContext.Models;
namespace MultipleDbContext.Repository;
public interface IBookRepository
{
void Add(Book entity,string contextName);
void Update(Book entity, string contextName);
List<Book> Get(string contextName);
}
We will select DbContext with the ContextName parameter.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using MultipleDbContext.Data;
using MultipleDbContext.Models;
namespace MultipleDbContext.Repository
{
public class BookRepository : IBookRepository
{
DbContextFactory _contexts;
public BookRepository(DbContextFactory contexts)
{
_contexts = contexts;
}
public void Add(Book entity, string contextName)
{
var context = _contexts.GetContext(contextName);
var addedEntity = context.Attach(entity);
addedEntity.State = EntityState.Added;
context.SaveChanges();
}
public void Update(Book entity, string contextName)
{
var context = _contexts.GetContext(contextName);
var updatedEntity = context.Entry(entity);
updatedEntity.State = EntityState.Modified;
context.SaveChanges();
}
public List<Book> Get(string contextName)
{
var context = _contexts.GetContext(contextName);
return context.Books.ToList();
}
}
}
In this class, we will move the DbContextFactory and DbContext objects into the Repository in the constructor. We can access the DbContext sent with the parameter. We will add the AutoFac IOC container to the project.
1
2
Install-Package Autofac -Version 6.3.0
Install-Package Autofac.Extensions.DependencyInjection -Version 7.2.0
After downloading the package, we will immediately configure AutoFac in Program.cs.
1
2
builder.Host.UseServiceProviderFactory(new AutofacServiceProviderFactory());
builder.Host.ConfigureContainer<ContainerBuilder>(b => b.RegisterModule(new AutoFacModule()));
We will add the AutoFacModule class.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class AutoFacModule : Module
{
protected override void Load(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
builder.RegisterType<DbOneContext>().As<BaseContext>();
builder.RegisterType<DbTwoContext>().As<BaseContext>();
builder.Register(ctx =>
{
var allContext = new Dictionary<string, BaseContext>();
allContext.Add("DbOneContext", ctx.Resolve<DbOneContext>());
allContext.Add("DbTwoContext", ctx.Resolve<DbTwoContext>());
return new DbContextFactory(allContext);
});
builder.RegisterType<BookRepository>().As<IBookRepository>();
}
}
After AutoFac IOC configuration, we will add a Web API controller named BookController to the controllers folder.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using MultipleDbContext.Models;
using MultipleDbContext.Repository;
namespace MultipleDbContext.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class BookController : ControllerBase
{
private IBookRepository _bookRepository;
public BookController(IBookRepository bookRepository)
{
_bookRepository = bookRepository;
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("{contextName}")]
public List<Book> Get([FromRoute] string contextName)
{
var books = _bookRepository.Get(contextName);
return books;
}
[HttpPost]
[Route("{contextName}")]
public IActionResult Post([FromRoute] string contextName,[FromBody] Book book)
{
try
{
_bookRepository.Add(book,contextName);
return Ok();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return BadRequest(e.Message);
}
}
[HttpPut]
[Route("{contextName}")]
public IActionResult Put([FromRoute] string contextName, [FromBody] Book book)
{
try
{
_bookRepository.Update(book, contextName);
return Ok();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return BadRequest(e.Message);
}
}
}
}
We select the dbContext with the contextName parameter. We will do CRUD operations with BookRepository. After creating the controller, we will create the DbOne and DbTwo databases with Migration. Since there are multiple DbContext files, it is necessary to specify which one to create in the migration process.
DbOneContext — Migration:
1
2
Add-Migration -Context DbOneContext
Update-Database -Context DbOneContext
DbTwoContext — Migration:
1
2
Add-Migration -Context DbTwoContext
Update-Database -Context DbTwoContext
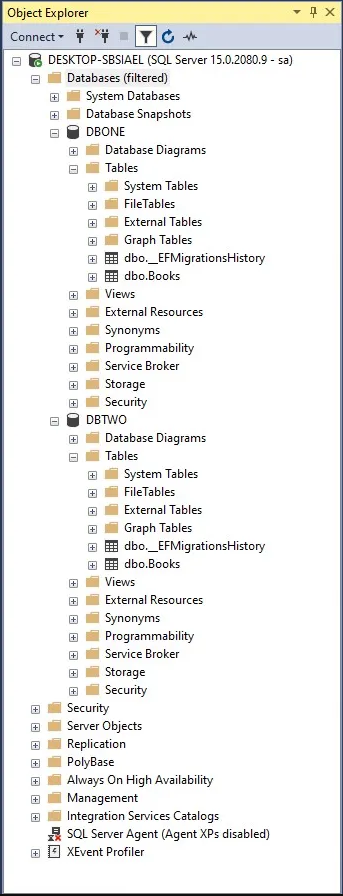
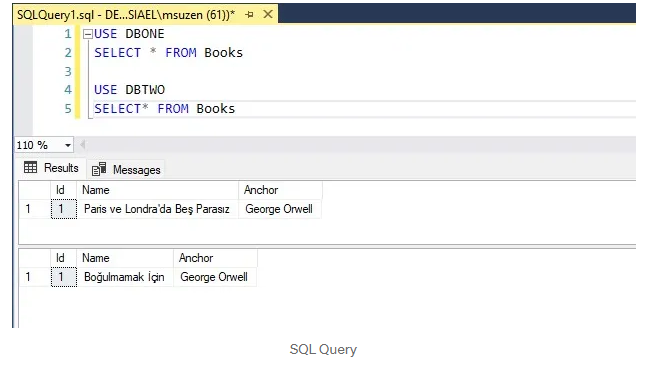
After the migration;
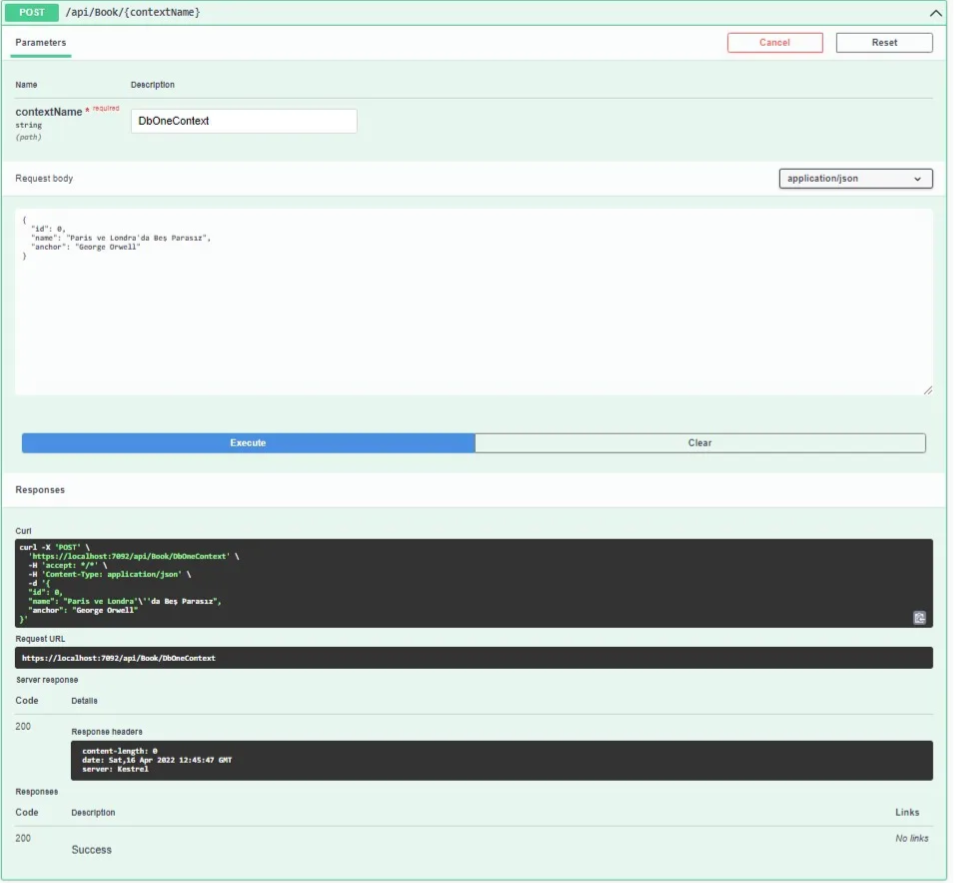
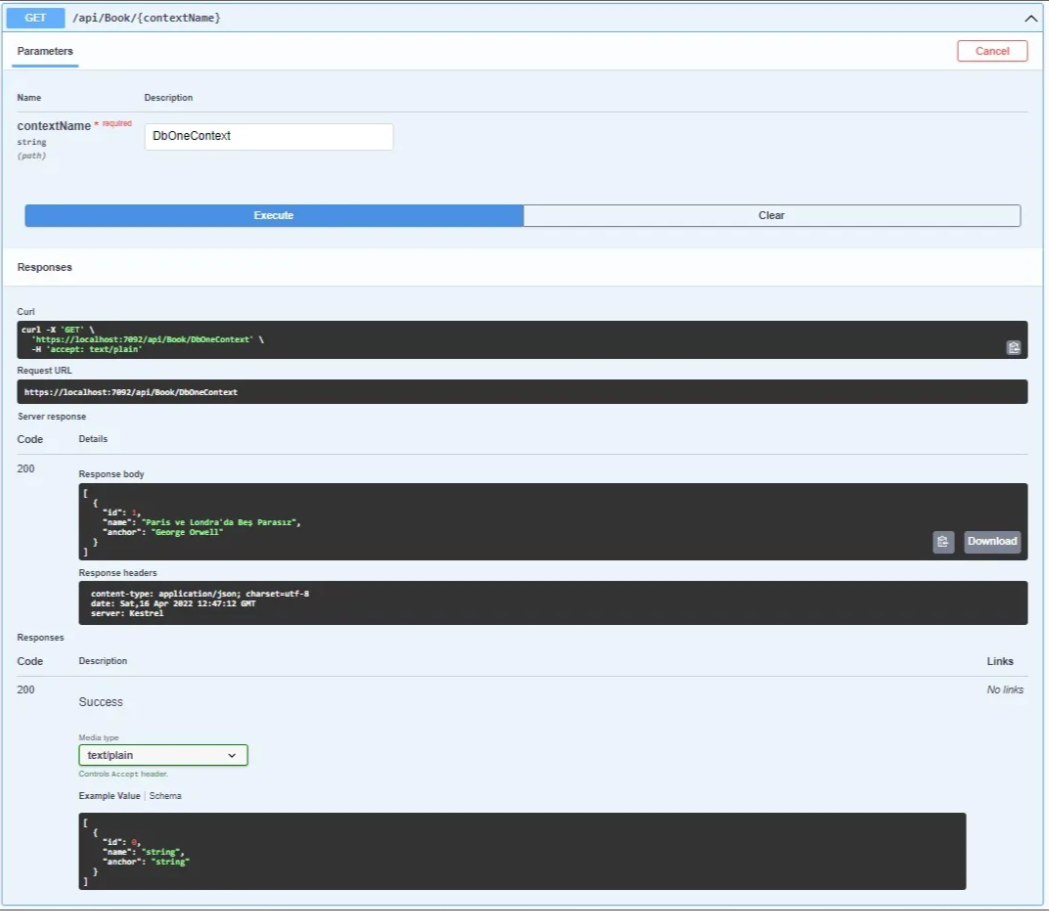
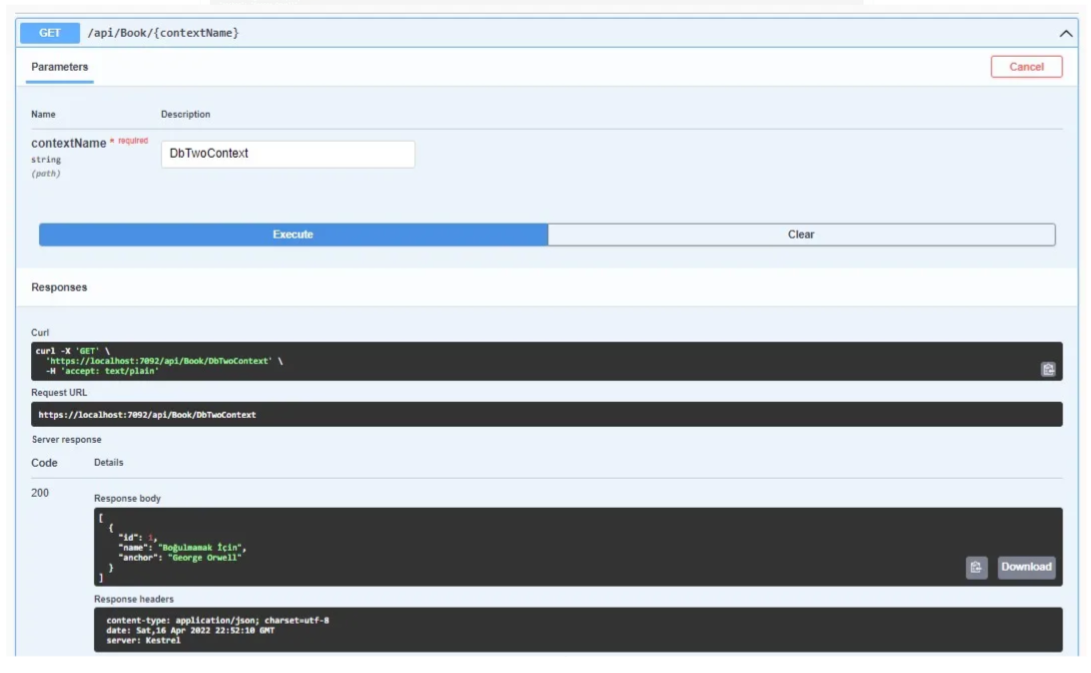
We will do CRUD operations with Swagger. We will do Post and Get requests for DbOneContext.
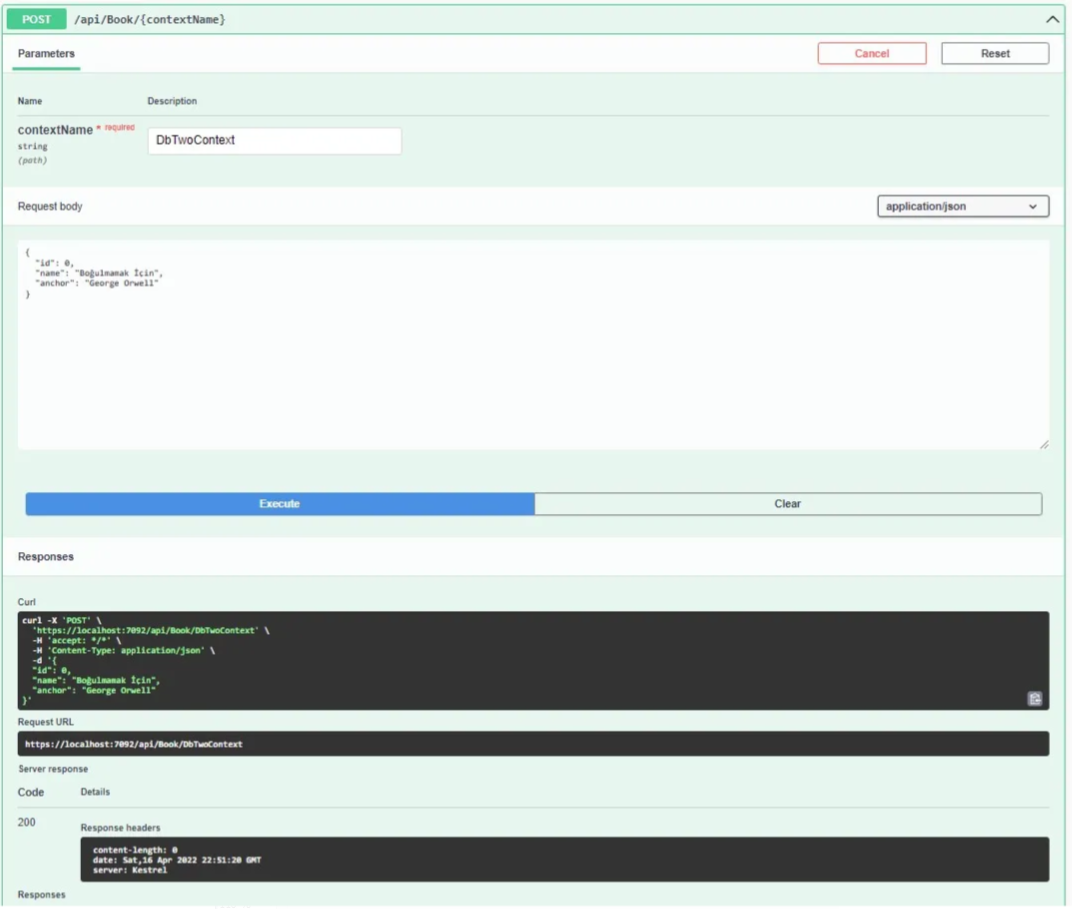
We will perform CRUD operations on the DbTwo database with the DbTwoContext parameter.
You can download the project here. Please let me know if there are typos in my post.