.NET Core ile Repository Pattern Kullanımı
Uygulama geliştirirken kullanıcıdan veri alır yada kullanıcıya veriler listeleriz. Bu verileri alırken yada listelerken herhangi bir veritabanından (ekleme,silme,güncelleme,listeleme) CRUD işlemleri yapıyoruz. Bu makalede .NET Core ile veritabanı işlemlerinde Repository Pattern yaklaşımını anlatmaya çalışacağım.
Repository Pattern Nedir?
Veritabanı işlemleri için yazdığımız kod bloklarının tekrar kullanımını sağlayan bir yaklaşımdır. Veritabanı işlemleri için sürekli farklı kodlar yazmaktansa, Repsitory Pattern yaklaşımı ile tekrar kullanabileceğimiz kod blokları sayesinde karmaşıklıktan kurtulup yönetilebilir bir yapı oluşturabiliriz. Örnek bir proje oluşturup yaklaşımı inceleyelim.
1
dotnet new sln
Yeni bir solution oluşturduktan sonra Core, Entities, DataAccess,Business katmanlarını ve WebAPI projesini oluşturacağım.
1
2
3
4
5
dotnet new classlib -o reppat.Core
dotnet new classlib -o reppat.Entities
dotnet new classlib -o reppat.DataAccess
dotnet new classlib -o reppat.Business
dotnet new webapp -o reppat.WebAPI
Core Katmanı
Tüm katmanlarda kullanılabilecek Extensions, Interfaces, Aspects vb yapıları içermektedir.
Entities Katmanı
Veri modellerinin (Entity,Dtos vb) içerdiği katmandır.
DataAccess Katmanı
Veri sağlayıcıları ile (SQL, MongoDb vb.) bağlantı kurabileceğimiz katmandır.
Business Katmanı
Veri katmanı ve proje arayüzü arasındaki köprü olan iş katmanıdır.
Projeyi ve katmanları Solution’a ekleyelim.
1
2
3
4
5
dotnet sln add reppat.WebAPI/reppat.WebAPI.csproj
dotnet sln add reppat.Core/reppat.Core.csproj
dotnet sln add reppat.Entities/reppat.Entities.csproj
dotnet sln add reppat.DataAccess/reppat.DataAccess.csproj
dotnet sln add reppat.Business/reppat.Business.csproj
Proje ve katmanların referanslarını ekleyelim.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
dotnet add reppat.Entities/reppat.Entities.csproj reference reppat.Core/reppat.Core.csproj
dotnet add reppat.DataAccess/reppat.DataAccess.csproj reference reppat.Core/reppat.Core.csproj
dotnet add reppat.DataAccess/reppat.DataAccess.csproj reference reppat.Entities/reppat.Entities.csproj
dotnet add reppat.Business/reppat.Business.csproj reference reppat.DataAccess/reppat.DataAccess.csproj
dotnet add reppat.WebAPI/reppat.WebAPI.csproj reference reppat.Core/reppat.Core.csproj
dotnet add reppat.WebAPI/reppat.WebAPI.csproj reference reppat.Entities/reppat.Entities.csproj
dotnet add reppat.WebAPI/reppat.WebAPI.csproj reference reppat.Business/reppat.Business.csproj
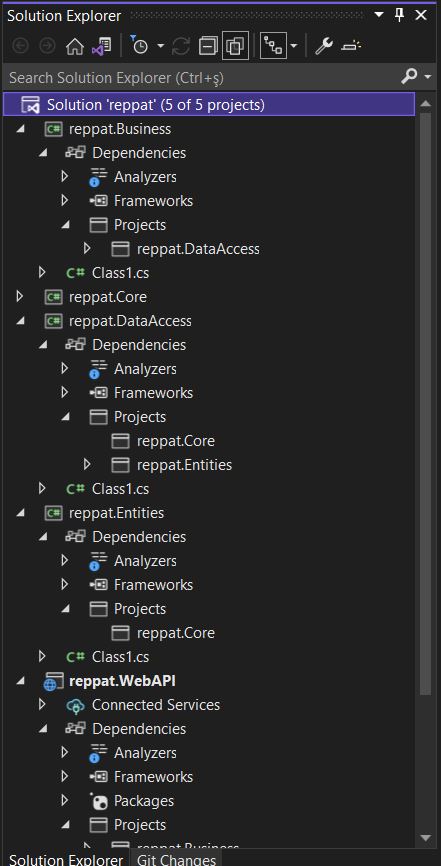
Referans eklemeleri tamamlandıktan sonra aşağıdaki gibi bir klasör ve ilişki yapısı olacaktır.
Proje sınıflarımızı oluşturduğumuza göre öncelikle Core katmanı ile başlayalım. Entities klasörü ve içerisine IEntity.cs isminde interface ekliyorum. IEntity sınıfının amacı birazdan geliştirmesini yapacağımız Repository Pattern prensibi için veri sınıflarını filtrelemektir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
namespace reppat.Core.Entities
{
public interface IEntity
{
}
}
IEntity interface’inin eklenmesinden sonra yine Core katmanına DataAccess klasörü ve içerisine IBaseEntityRepository isminde bir interface ekliyorum. Bu interface Repository Pattern yapısının temelini oluşturmaktadır.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
using reppat.Core.Entities;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace reppat.Core.DataAccess
{
public interface IBaseEntityRepository<T> where T : class, IEntity, new()
{
T Get(Expression<Func<T, bool>> filter);
List<T> GetList(Expression<Func<T, bool>> filter = null);
T Add(T entity);
T Update(T entity);
void Delete(T entity);
void AddRange(List<T> entities);
}
}
Yukarıdaki kod bloğunu inceleyelim. IBaseEntityRepository’den türeyebilecek (implement edilebilecek) sınıflar için bir where koşulu bulunmaktadır. Bu where koşulu görüldüğü gibi T objesinin bir class ve new() yani instance alınabilecek bir sınıf olması gerekmektedir. Ayrıca daha önceki kod bloğunda tanımladığımız IEntity interface’inden türeyen sınıfları içermesi gerekmektedir. Bu şekilde bir sınıfın filtrelenmesi sağlamaktadır. Metodları incelediğimizde bir Expression filtresi görüyoruz. Bu filteler ile veritabanından tüm veri getirilmeden önce bir filtre gönderilerek sadece istenilen bilgilerin listelenmesi sağlanmaktadır.
Veritabanı işlemlerini genellikle ORM (Entity Framework, Hibernate vb.) araçları ile yapıyoruz. Kullandığımız ORM aracına göre Core katmanında klasör oluşturuyorum. Ben EntityFramework isminde bir klasör oluşturup içerisine EfBaseEntityRepository isminde bir sınıf ekliyorum. EfBaseEntityRepository sınıfını IBaseEntityRepository interface’den türetiyoruz. Core katmanına nuget paket yönetimi ile Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore paketini ekliyorum.
1
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore -Version 6.0.0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using reppat.Core.Entities;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace reppat.Core.DataAccess.EntityFramework
{
public class EfBaseEntityRepository<TEntity, TContext> : IBaseEntityRepository<TEntity>
where TEntity : class, IEntity, new()
where TContext : DbContext, new()
{
public TEntity Add(TEntity entity)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void AddRange(List<TEntity> entities)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void Delete(TEntity entity)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public TEntity Get(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public List<TEntity> GetList(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter = null)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public TEntity Update(TEntity entity)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
Yukarıdaki kod bloğunu inceleyelim. Görüdüğü gibi TEntity ve TContext isimlerinde iki parametre alan bir sınıf oluşturduk. TEntity parametresi IEntity interface’inden türetilen ve instance alınabilecek sınıf tipinde olacağını where koşulu ile anlayabiliyoruz. TContext isimli parametresinin instance alınabilen ve Entity Framework ORM aracının veritabanı işlemlerini yapılandırabildiğimiz DbContext tipinde olacağını görüyoruz. Parametreleri inceledeğimize göre metodları geliştirme işlemine geçebiliriz.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public TEntity Get(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter)
{
using (var context = new TContext())
{
return context.Set<TEntity>().SingleOrDefault(filter);
}
}
Parametre olarak gönderilen TEntity, sınıfın where koşulundan geçtiğine göre artık bu sınıfn bir DbContext içerisindeki DbSet ile tanımlanan entity olduğunu biliyoruz. Böylece using bloğunda context isminde aldığım instance ile, DbContext’in Set metoduna TEntity’i tanıtıp SingleOrDefault yada FirstOrDefault metodları ile parametreden gelen Expression filtresini veriyorum. Get metodu gönderdiğimiz filtreye uygun olarak kayıtlarımızı geri döndürecektir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public List<TEntity> GetList(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter = null)
{
using (var context = new TContext())
{
return filter == null ? context.Set<TEntity>().ToList() : context.Set<TEntity>().Where(filter).ToList();
}
}
Get metodunda olduğu gibi GetList metodunda da aynı işlemleri yapıyorum. Burada farklı olarak filter parametresi eğer gönderilmezse ve null ise ToList() metodu ile tüm listeyi geri döndürüyorum.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public TEntity Add(TEntity entity)
{
using (var context = new TContext())
{
var addedEntity = context.Entry(entity);
addedEntity.State = EntityState.Added;
context.SaveChanges();
}
return entity;
}
Add metodunda yaptığım işlem parametre olarak gönderilen TEntity tipindeki entity objesini Context’in Entry metodu ile DbContext’e eklenmesini sağlıyorum ve State = EntityState.Added tanımı ile yeni kayıt ekleneceğini iletiyorum. Daha sonra context.SaveChanges(); metodu ile kayıt işlemini tamamlamış oluyoruz.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public TEntity Update(TEntity entity)
{
using (var context = new TContext())
{
var updatedEntity = context.Entry(entity);
updatedEntity.State = EntityState.Modified;
context.SaveChanges();
}
return entity;
}
Update metodunda Add işlemlerinin aynısını yapıyorum. Fakat buradaki farklı olan kısım görüldüğü üzere State = EntityState.Modified tanımı. Bu tanım ile DbContext’e gönderilen objenin yani veritabanı tablosunun güncelleneceğini iletiyorum. Burada kısa bir bilgiyle Entry ve Attach farkına değinmek istiyorum. Attach metodu ile gönderilen veritabanı tablo objesinin sadece değişen alanların güncellenmesi sağlanır. Ancak Entry metodu tam tersine gönderilen objenin tüm alanlarını güncelleme işlemi isteğidir. SaveChanges() ile işlem yapılmış olur. Siz uygulamanızın performans yapılandırmasına göre farklı tercih edebilirsiniz.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void Delete(TEntity entity)
{
using (var context = new TContext())
{
var deletedEntity = context.Entry(entity);
deletedEntity.State = EntityState.Deleted;
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
Delete metodunda gönderilen entity State = EntityState.Deleted tanımı ile silinecek olarak işaretlenip SaveChanges() metodu ile silme işlemi tamamlanıyor.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public void AddRange(List<TEntity> entities)
{
using (var context = new TContext())
{
using (var transaction = context.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
foreach (TEntity entity in entities)
{
var addedEntity = context.Entry(entity);
addedEntity.State = EntityState.Added;
}
context.SaveChanges();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
transaction.Rollback();
throw e.GetBaseException();
}
transaction.Commit();
}
}
}
AddRange metodunu üzerinde çalıştığım bir projede ihtiyaç dahilinde kullandığım için sizlerle paylaşmak istedim. Bu kod bloğu ile birden fazla TEntity parametresinin bir transaction bloğu açarak ekleme işemini yapıyorum. Herhangi bir adımda hata ile karşılaşdığında transaction.Rollback() metodu ile yapılan tüm işlemler geri alınmaktadır. Yazdığımız EfBaseEntityRepository sınıfı sayesinde Repository Pattern altyapısını belli ölçüde geliştirmiş olduk.
DataAccess katmanında veritabanı işlemlerini yapmak için geliştirmeye devam edelim. Interface ve bu interface’lerden türeyecek service sınıfları için DataAccess katmanına Abstract ve Concrete isimli iki klasör oluşturuyorum. Concrete klasörünün içerisine kullandığım ORM EntityFramework olduğu için EntityFramework isimli bir klasör oluşturup onunda içerisine Context isimli bir klasör ekliyorum. Context klasörüne reppatContext isminde bir sınıf ekliyorum. Bu sınıfı DbContext’ten türetip ilgili configuration ayarlarını ekliyorum.
1
2
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -Version 6.0.0
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore -Version 6.0.0
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore ve Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer paketlerinin kurulumunu yapıyorum. OnConfiguring metodunu override yapıp veritabanı bağlantısını ekliyorum.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace reppat.DataAccess.Concrete.EntityFramework.Contexts
{
public class ReppatContext : DbContext
{
public ReppatContext()
{
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=REPPAT;User ID=sa;Password=Pw123456");
}
}
}
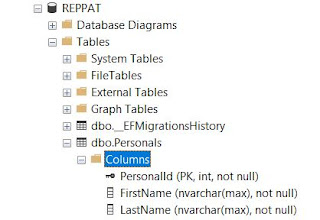
Bağlantı ayarlarını eklediğimize göre Entities katmanında tablo yapılarını içeren sınıfları oluşturabiriz. Ben bir tablo ile örnek yapmak istiyorum. Bu nedenle Entities katmanına Concrete isminde bir klasör oluşturup Personal isimli bir sınıf ekliyorum. Bu örnek projenin personel kart bilgilerini içeren bir sınıf olacak.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
using reppat.Core.Entities;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace reppat.Entities.Concrete
{
public class Personal : IEntity
{
public int PersonalId { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
}
Personal sınıfını DbSet ile ReppatContext içerisine tanımlıyorum.
1
public DbSet<Personal> Personals { get; set; }
Migration ile veritabanı ve personal tablosunu oluşturalım. Migration oluşturmadan önce eklememiz gereken bir paket bulunmaktadır. DataAccess katmanına Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tool paketini ve WebAPI projemize Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design paketini ekliyorum.
1
2
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools -Version 6.0.0
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design -Version 6.0.0
1
Add-Migration initial
Yukarıdaki kod ile initial isminde bir migration sınıfı oluşturuluyor. Update-Database komutu ile veritabanı ve Personals tablosunu oluşturuyorum.
DataAccess katmanında Abstract klasöründe IPersonalDal isminde interface ekliyorum. IBaseEntityRepository interface’inden türetip parametre olarak istediğimiz IEntity tipindeki Personal sınıfını veriyorum.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
using reppat.Core.DataAccess;
using reppat.Entities.Concrete;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace reppat.DataAccess.Abstract
{
public interface IPersonalDal : IBaseEntityRepository<Personal>
{
}
}
Daha sonra Concrete klasörüne EfPersonalDal isminde bir sınıf ekliyorum. EfBaseEntityRepository sınıfından türetip IEntity tipinde ve DbContext tipinde iki parametre istediğim için Personal ve ReppatContext sınıflarını gönderiyorum. Aynı zamanda IPersonalDal interface’inden türeyeceğini de belirityorum. Bu şekilde IPersonalDal interface’inin türetildiği interface IBaseEntityRepository ve EfPersonalDal sınıfının türediği interface IPersonalDal sayesinde IBaseEntityRepository olmaktadır. EfBaseEntityRepository referansı ile IBaseEntityRepository impelementini kullanacağını belirtmiş oluyorum. İşte bu şekilde bir kez yazdığımız EfBaseEntityRepository implementasyonu ile oluşturduğumuz sınıflarda tekrar tekrar kullanabiliyoruz.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
using reppat.Core.DataAccess.EntityFramework;
using reppat.DataAccess.Abstract;
using reppat.DataAccess.Concrete.EntityFramework.Contexts;
using reppat.Entities.Concrete;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace reppat.DataAccess.Concrete.EntityFramework
{
public class EfPersonalDal : EfBaseEntityRepository<Personal,ReppatContext>,IPersonalDal
{
}
}
DataAccess katmanında veri sınıflarını oluşturduğumuza göre artık iş katmanını geliştirmeye geçebiliriz. Business katmanında Abstract ve Concrete klasörlerini ekliyorum. Abstract klasörüne IPersonalService isminde bir interface ekliyorum.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
using reppat.Entities.Concrete;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace reppat.Business.Abstract
{
public interface IPersonalService
{
Personal Get(int personalId);
List<Personal> GetList();
Personal Add(Personal personal);
Personal Update(Personal personal);
}
}
IPersonalService interface’ini ekledikten sonra Concrete klasörüne PersonalManager sınıfını ekliyorum.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
using reppat.Business.Abstract;
using reppat.DataAccess.Abstract;
using reppat.Entities.Concrete;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace reppat.Business.Concrete
{
public class PersonalManager : IPersonalService
{
IPersonalDal _personalDal;
public PersonalManager(IPersonalDal personalDal)
{
_personalDal = personalDal;
}
public Personal Add(Personal personal)
{
return _personalDal.Add(personal);
}
public Personal Get(int personalId)
{
return _personalDal.Get(x=>x.PersonalId == personalId);
}
public List<Personal> GetList()
{
return _personalDal.GetList();
}
public Personal Update(Personal personal)
{
return _personalDal.Update(personal);
}
}
}
Yukarıdaki kod bloğunda görüldüğü üzere IPersonalDal interface’i constructor ile parametre olarak alıyorum. Ancak _personalDal’ın instanceini almadığımız için bu şekilde bir projede kullandığımızda hata alacağız. Bunun için Dependency Injection ile IPersonalDal istediğimizde EfPersonalDal sınıfını kullanılmasını sağlayacağız. WebAPI projemizi geliştirmeye başlayalım.
WebAPI projemizde Controller klasörüne PersonalController isminde bir API Controller ekliyorum ve içeriğini aşağıdaki gibi geliştiriyorum.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using reppat.Business.Abstract;
using reppat.Entities.Concrete;
namespace reppat.WebAPI.Controllers
{
[Route("[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class PersonalController : ControllerBase
{
IPersonalService _personalService;
public PersonalController(IPersonalService personalService)
{
_personalService = personalService;
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Add(Personal personal)
{
if (personal == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(personal));
try
{
_personalService.Add(personal);
return Ok();
}
catch (Exception exp)
{
return BadRequest(exp.Message);
}
}
[HttpPut]
public ActionResult Update(Personal personal)
{
if (personal == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(personal));
try
{
_personalService.Update(personal);
return Ok();
}
catch (Exception exp)
{
return BadRequest(exp.Message);
}
}
[HttpGet("Get/{personalId}")]
public Personal Get(int personalId)
{
return _personalService.Get(personalId);
}
[HttpGet]
public List<Personal> GetList()
{
return _personalService.GetList();
}
}
}
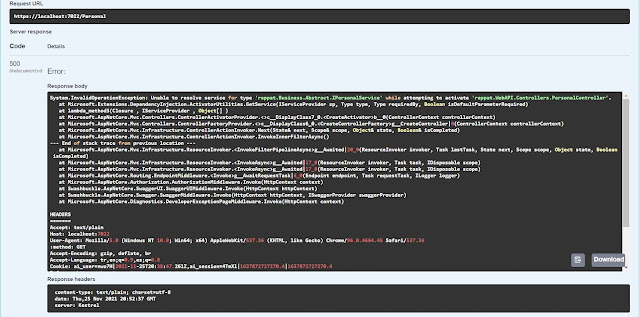
Bu şekilde projeyi çalıştırıp Swagger yardımıyla test yaptığımızda aşağıdaki hatayı alıyorum.
Bu hatayı daha önce belirttiğim gibi Dependency Injection ayarlarını yapmadığım için alıyorum. Program.cs içerisinde builder ile Singleton tanımını yapıyorum.
1
2
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IPersonalDal, EfPersonalDal>();
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IPersonalService, PersonalManager>();
Tanımlamaları yaptıktan sonra projeyi çalıştırıp bir personel ekleme işlemini yapıyorum ve sıkıntısız bir şekilde sonuç alıyorum. Repository Pattern konusunu .NET Core ile incelemiş olduk. Makale biraz uzun olduğu için umarım sıkılmamışsınızdır. Uygulamayı buradan indirebilirsiniz. Bir sonraki makalede görüşmek üzere.